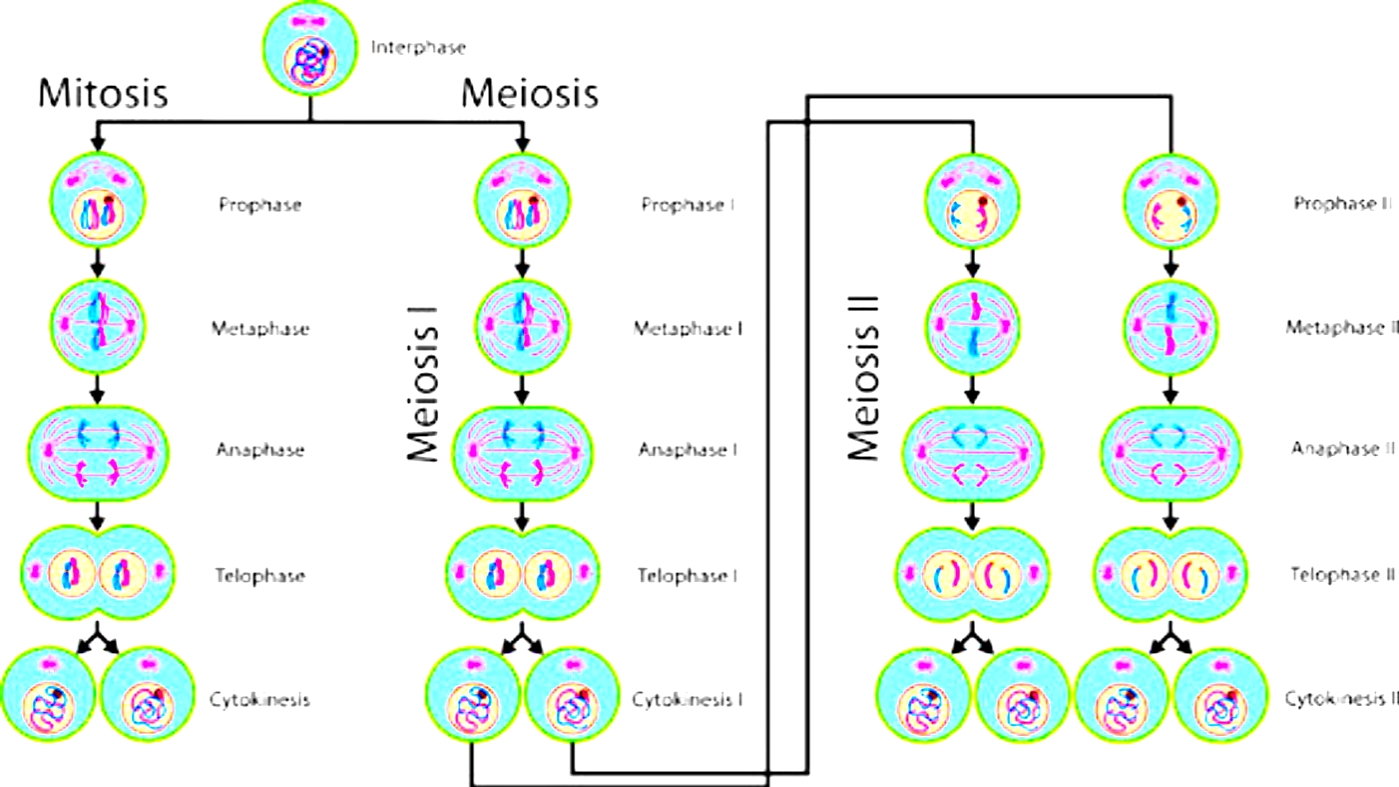
Mitosis versus meiosis
Cells partition and duplicate in two ways, mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis brings about two indistinguishable little girl cells, while meiosis brings about four sex cells.
Underneath we feature the keys distinctions and likenesses between the two kinds of cell division.
Differences
Mitosis
- Includes one cell division
- Brings about two girl cells
- Brings about diploid girl cells(chromosome number continues as before as parent cell)
- Little girl cells are hereditarily indistinguishable
- Happens in all living beings with the exception of infections
- Makes all body cells (physical) aside from the microorganism cells (eggs and sperm)
- Prophase is a lot more limited
- No recombination/getting over happens in prophase.
- In metaphase individual chromosomes (sets of chromatids) line up along the equator.
- During anaphase the sister chromatids are isolated to inverse shafts.
Meiosis
- Includes two progressive cell divisions
- Brings about four girl cells
- Brings about haploid girl cells (chromosome number is split from the parent cell)
- Little girl cells are hereditarily unique
- Happens just in creatures, plants and organisms
- Makes microbe cells (eggs and sperm) as it were
- Prophase I takes significantly longer
- Includes recombination/getting over of chromosomes in prophase I
- In metaphase I sets of chromosomes line up along the equator.
- During anaphase I the sister chromatids move together to a similar shaft.
- During anaphase II the sister chromatids are isolated to inverse posts.
Similarities
Mitosis
- Diploid parent cell
- Comprises of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
- In metaphase individual chromosomes (sets of chromatids) line up along the equator.
- During anaphase the sister chromatids are isolated to inverse shafts.
- Closes with cytokinesis.
Meiosis
- Diploid parent cell
- Comprises of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase (yet two times!)
- In metaphase II individual chromosomes (sets of chromatids) line up along the equator.
- During anaphase II the sister chromatids are isolated to inverse shafts.
- Closes with cytokinesis.







0 Comments